From Schema to Snippets: A Blueprint for Chatbot
Building Efficient Chatbots: The 3 Essential Steps Every Business Should Follow After ChatGPT
When designing conversational user experiences, there is often a focus on making chatbots smart, intelligent, and human-like. However, this approach can be driven more by technology constraints than the actual services being provided. While language models like ChatGPT can enhance customer experience, they can not determine the business logic of the chatbot, which requires a deep understanding of specific industry requirements and goals.
Given the advent of ChatGPT, what is the recommended approach to chatbot design that promotes logical and helpful conversations?
Service-driven Approach
The foundation of a chatbot is its service, which determines the tasks it can perform and how it interacts with customers. For example, a restaurant owner developing a chatbot to assist customers in booking reservations needs to design the service logic to ensure that the chatbot can accurately identify available time slots, check for scheduling conflicts with the restaurant's tables, and confirm bookings with customers.
User: "Hi, I'd like to make a reservation for two people tonight at 7 pm."
Chatbot: "Great, we'd be happy to help you make a reservation. I have checked our availability and unfortunately we are fully booked at 7 pm tonight. However, we do have availability at 6 pm or 8 pm. Would either of those times work for you?"
User: "Hmm, neither of those times work for me. How about 7:30 pm?"
Chatbot: "Let me check. I'm sorry, but we don't have any available tables at 7:30 pm either. Would you like me to check other days or times for you?"
User: "How about Thursday at 7 pm?"
Chatbot: "I'm sorry, we're fully booked on Thursday at 7 pm as well. However, we do have availability on Friday at 7 pm. Would you like to reserve a table for Friday instead?"
User: "Yes, that works."
Chatbot: "Great! I have reserved a table for you at our restaurant on Friday at 7 pm. Can I confirm your reservation under the name of John?"
User: "Yes, that's correct."
Chatbot: "Perfect! Your reservation is confirmed and we look forward to seeing you on Friday. Is there anything else I can assist you with?"
User: "No, that's all. Thank you so much for your help!"
Chatbot: "You're welcome. Have a great day and we'll see you on Friday!"To achieve consistency, logic, and helpfulness in chatbot interactions, it is important to adopt a service-driven design approach. This approach provides a clear framework for chatbot responses, addressing questions such as when to present options, seek clarification, or confirm requests. To accomplish this, chatbots need to recognize key user request types, such as number of people, date, and time, and declare specific interactions using CUI (conversational user interface) components, like prompts, recommendations, confirmations and value clarifications.
Following this approach enables chatbots to deliver a predictable and consistent experience for customers, resulting in a more satisfying conversational experience aided by language models such as ChatGPT that generates responses aligned with the service logic, making the process of building chatbots much easier and enabling businesses to provide high-quality service experiences to their customers.
The following strategy outlines how to achieve service-driven design.
1. Start From Schema
Starting with a schema representation of the service can be helpful to ensure that chatbot conversations with customers are efficient and structured. The schema outlines all the required slots and their types, which determine the information that needs to be collected from customers.
For example, a restaurant reservation chatbot might require slots for the number of people, date and time, and any special requests or dietary restrictions. Similarly, a healthcare appointment scheduling chatbot might require slots for the type of appointment, preferred date and time, location, and insurance information.
 The scheme representation of a simple restaurant reservation service
The scheme representation of a simple restaurant reservation service
By starting with the schema, the chatbot can ensure that it collects all the necessary information in a logical and efficient manner. Once the schema is established, the chatbot can move on to determining the logic of the interaction, which will help to further refine the conversational experience for customers.
2. Determine Interaction Logic
Determining the interaction logic is crucial for effectively collecting the required information from customers. This may involve asking a series of questions or presenting options for each slot. For instance, a restaurant reservation chatbot can confirm each piece of information before moving on to the next, while a healthcare chatbot can ask clarifying questions and provide appropriate recommendations for treatment or referral to a doctor.
The conversational behaviors that are commonly used in interactions can be implemented as CUI components, including prompt, recommendation, confirmation, value clarification, and more. These components can be combined and reused to create a variety of conversational interactions for any service:
- Prompt: prompts are used to ask customers for input, such as asking for their name, email address, or other required information. For example "What time should I book the table tomorrow?"
- Recommendation: recommendations are used to provide users with options to choose from, such as a list of products or services.
- Validation: validations are used to inform customers when there is a problem with their input or action, such as when they provide an invalid email address, and make sure they are not stuck in a loop if their input isn't accepted. For example, "Sorry, the time you want to book is not available at present. What time should I book the table tomorrow?"
- Confirmation: confirmations are used to confirm customer input or verify that the customer wants to perform a certain action. Confirmation can be used in implicit (“Alright, 4 guests. [...]”) or explicit (“I understood 4 guests, is that correct?”) way to make sure chatbot gets everything right.
- ……
By using these CUI components, chatbots can deliver a more effective and satisfying conversational experience for customers.
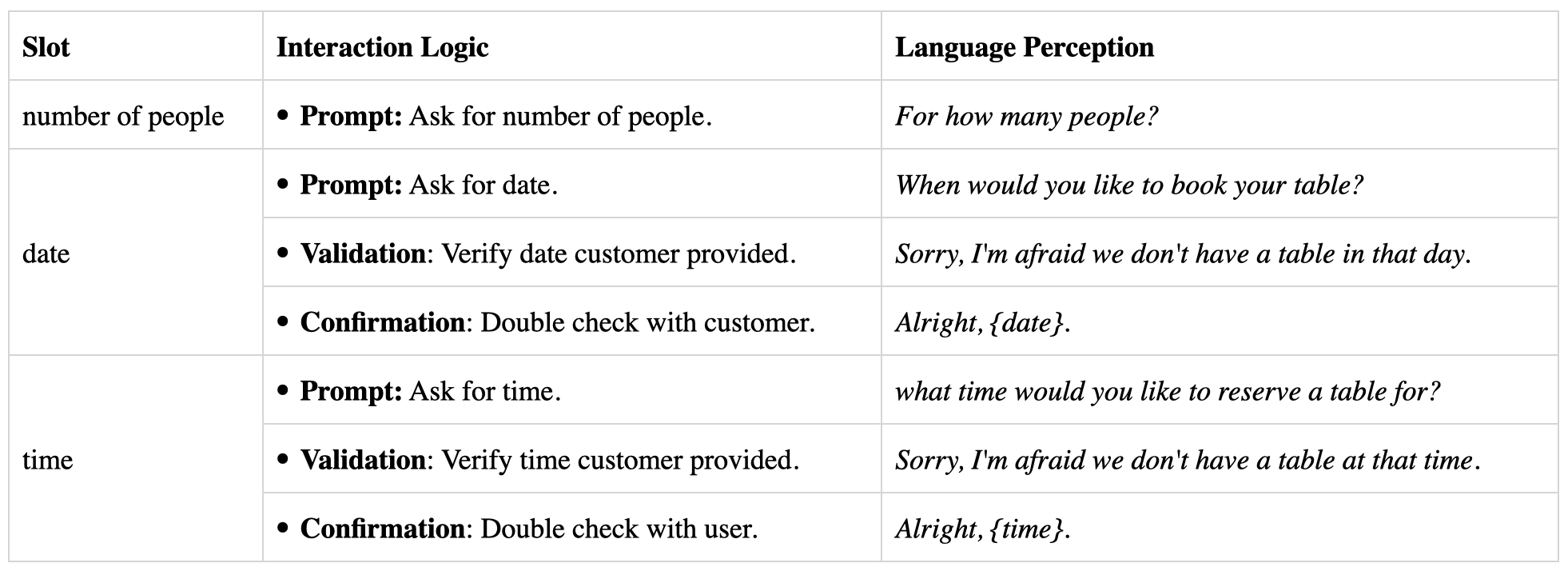 The interaction logic for a restaurant reservation service
The interaction logic for a restaurant reservation service
After determining the interaction logic, language-related components such as templates for text generation and utterance exemplars for dialog understanding become essential. By optimizing the use of language model technology, such as ChatGPT, for structured conversations that follow a predetermined framework or utilizing magic zero-shot learning to improve chatbots' understanding of user inquiries, businesses can reduce the cost of building functional chatbots significantly. This approach enables businesss to focus solely on interaction logic, leading to a more efficient and cost-effective chatbot building process.
Once the schema representation and interaction logic are determined, the conversational experience can be described as contextual snippets.
3. Describe Contextual Snippet
Contextual snippet is a better approach than a dialogue flow when dealing with complex conversations that involve multiple topics. The reason is that as the number of topics increases, the dialogue possibilities grow exponentially, making it impractical to map out every step a customer might take in a dialogue flow.
Contextual snippets, on the other hand, describe the conversational behavior in small, manageable pieces, which businesss can use to build a more flexible and adaptive chatbot. Instead of worrying about the dialogue flow and how the customer arrived at a certain point in the conversation, business can focus on the behavior required at each stage of the interaction. This allows them to better handle unpredictable customer responses and provide a more personalized experience.
Furthermore, contextual snippets can be combined and reused to create a variety of conversational interactions for any service. This modularity allows businesses to build and test chatbot components independently and iterate quickly. It also makes it easier to scale chatbots to new domains or services, as existing snippets can be adapted or combined to fit new requirements.
Let's use a restaurant reservation service as an example:
Happy path
Starting with the happy path is a good approach, and as you encounter rare corner cases, you can gradually incorporate their requirements. It is not necessary to modify the happy path requirement to accommodate these new corner cases. The common use cases may look like the following:
 Snippet 1: Happy path
Snippet 1: Happy path
Error handling
Designing error handling and recovery procedures is crucial for situations when tables are unavailable or customers provide incorrect information. The chatbot should gracefully handle such issues and provide helpful responses to customers. Consider the following examples:
 Snippet 2: Specified information does not pass validation
Snippet 2: Specified information does not pass validation
Make changes
The process of modifying or cancelling a reservation should be made simple and user-friendly for customers. For instance, in case a customer decides to alter their reservation:
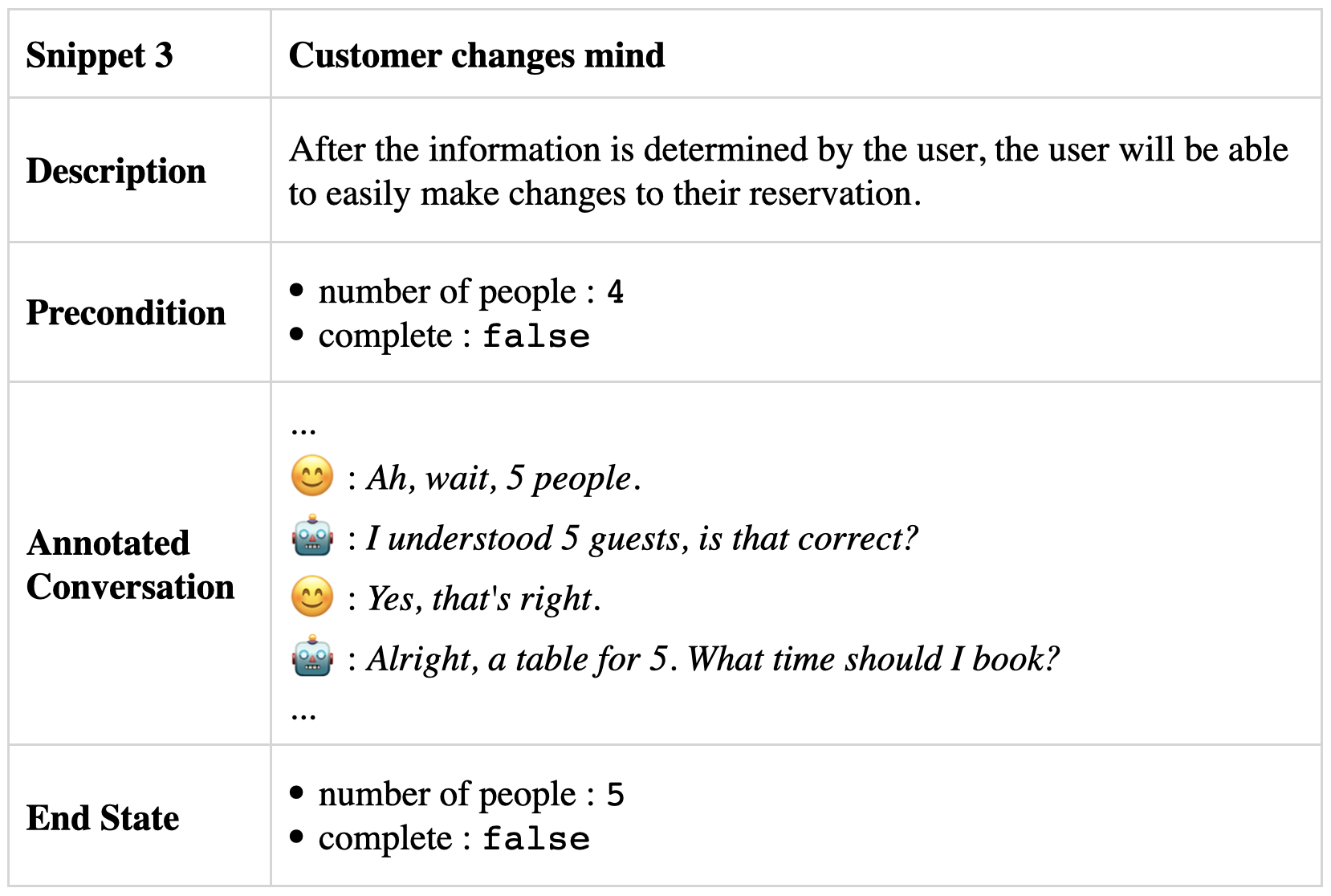 Snippet 3: Customer changes mind
Snippet 3: Customer changes mind
The above is just an example, you can expand your snippet according to actual scenarios.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a service-driven approach that starts with schema representation, determines interaction logic, and describes contextual snippets is crucial when designing a chatbot for a business. These steps help ensure that the chatbot collects all the necessary information from customers in an efficient and streamlined manner. By focusing on the behavior required at each stage of the interaction, business can incrementally build a conversational experience that accurately captures the expected conversational behavior for delivering services. This method also enables businesses to optimize the use of language model technology, such as ChatGPT, to enhance chatbot performance, leading to a significant reduction in the cost of building functional chatbots. Overall, this approach provides a more efficient and effective way to design chatbots that can improve the customer experience and help businesses achieve their goals.
Reference:
