Overview
OpenCUI is a practical framework for building applications with a conversational user interface. At a high level, it adopts a dual-process approach, utilizing Large Language Models (LLMs) to address informational or low-impact queries through prompt engineering. For high-impact and transactional queries, it relies on software engineering. Through the integration of LLM-based dialog understanding and schema-based interaction logic, OpenCUI facilitates cost-effective development of natural and reliable conversational experiences.
OpenCUI is specially designed to aid in building 'copilots,' which function as conversational companions for your existing apps. Unlike regular chatbots that directly trigger backend APIs upon request, copilots provide information and frontend action buttons to guide users through app interactions. This allows you to address existing UX issues without the need to rebuild everything for a conversational user interface. As copilots respond to natural language requests, they eliminate the steep learning curve typically associated with feature-rich applications. Furthermore, copilots offer context-dependent assistance, reducing the effort required for both new and casual users to derive value from your application.
Life of a copilot query
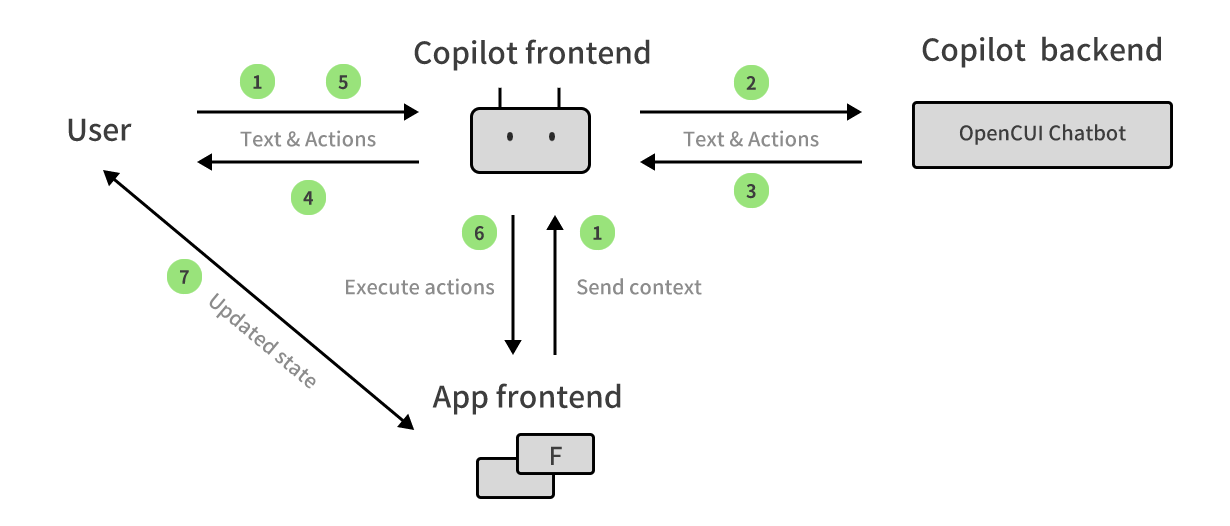
The user query handling process involves the following steps:
- The user inputs text to the copilot frontend, the copilot frontend also query your app for the context where users are in your app.
- The copilot frontend passes the user query and context to the copilot backend.
- Based on the predefined skills, the copilot backend responds with relevant text and suggested actions to the copilot frontend.
- The copilot frontend displays the text and suggested actions to the user.
- The user clicks a specific suggested action.
- The app frontend executes the action requested by the copilot frontend.
- The app frontend bring user to the target state, saving user from figuring out how to do this.
Copilot is typically developed using the same client/server architecture: there will be copilot frontend that coexists with your app's frontend, and then there will be a copilot backend, or simply a special chatbot that you can build using OpenCUI. As conversational companion to your application, copilot needs to interact with your application in order to provide context dependent help to your user. The interaction between the copilot and your application is defined by the following meta API served by your application:
fun get_state(): List<FrameEvent> // This function simply return the state in json form.
fun execute(action_in_json: Action) // This function execute the action defined in the json format.To build a copilot for your app, you just need to complete the follow two steps:
- Implement copilot meta API in your app: You need to design the type system to describe the interaction state and frontend action so that user can drive through natural language command.
- Build copilot backend: This can be done by attaching dialog annotations to function schemas to so that copilot follows the desired interaction logic.
For most use cases, you can use our reference implementation of copilot frontend (currently only web version) since copilot frontend does not need understand the semantics of copilot meta API. This reference implementation is based on copilot meta API and OpenCUI SDK for interaction with copilot backend. The reference implementation are open sourced so that you can check out in case you need to make modification.
