Build a copilot backend
This guide will demonstrate how to build a copilot backend, or simply chatbot, using the OpenCUI platform, taking OpenCUI copilot as an example. The OpenCUI copilot is designed to provide onboarding and feature discovery for causal chatbot developer. Copilot is a special chatbot in that it helps user indirectly instead of doing things directly on user's behalf.
To gain a basic understanding, it is important to first learn key concepts about type systems and dialog annotations. Unlike other flow based approach, OpenCUI allow you to build effective conversational user interface in a schema grounded fashion, based on the observation that all user interaction are designed to create function object based on user input. This object can then be invoked to deliver the service to user. Under this approach, it is all about defining the type and attach dialog annotation to make that type, including primitive type(entities), composite type(frames) and function(skills), instantiable via conversation. These dialog annotations specify how builders want each slot, also known as component or member data, can be instantiated through conversation, and OpenCUI runtime will manage the conversation so that your bot can deliver the service to user as quickly as possible.
Build entities
In this tutorial, we will thus describe the types needed to build a copilot for OpenCUI itself. Since the main objects that builders work with on the platform are entity, frame and skill, we need to introduce some entities that so builders can talk about them. For instance, an entity called "FrameType" is created to identify all frames and skills. The full list of the entity types we introduce is as follows.
Details with OpenCUI Copilot as an example
Create the following entities:
FrameType: It represents the frame and skill types in current projects.EntityType: It represents the entity types in current projects.SlotEntity: It represents the slots in current projects.
Note, because each project on OpenCUI had different types, these three entity types need to be declared as dynamic so that the instance is pushed at runtime from actual chatbot. But for most application, you only need static entities.
Build frame for context
Each application requires different data structure to capture the current interaction state, conceptually a stack of GUI pages. For OpenCUI, since builder are mainly work with types and their slots, and types are organized into projects and organizations, we introduce a frame called "PageContext" and add slots like orgLabel, agentLabel, and page in this frame. Additionally, we add a typeLabel slot with type FrameType. The OpenCUI copilot frontend can encode the state of current user session into frame event, so context
of "PageContext" frame will be automatically filled for each turn.
Details with OpenCUI Copilot as an example
Create a frame with label
PageContext.Add the following slots in this frame:
orgLabelwith typeStringagentLabelwith typeStringpagewith typeStringtypeLabelwith typeFrameType- ...
Build skills to help user
Skills are functionalities that can be triggered by users through natural language requests. This section illustrates the process of building a conversational experience to guide user through cloning an echo chatbot.
Build clone skill
To build a skill that can be triggered conversationally, follow these steps:
- Create a new skill and add the expression to trigger it.
- Add context if it's required.
- Add parameters needed to execute a specific action.
- Add a slot to verify if the app users are in the target state or on the target page.
- Specify the action(s) for app users to execute.
Instead of building everything from scratch, OpenCUI allows you to build bigger conversational experience by compose smaller ones together. Let's consider the CloneProject skill used to guide app users in cloning a project. The happy path for CloneProject skill involves the following steps:
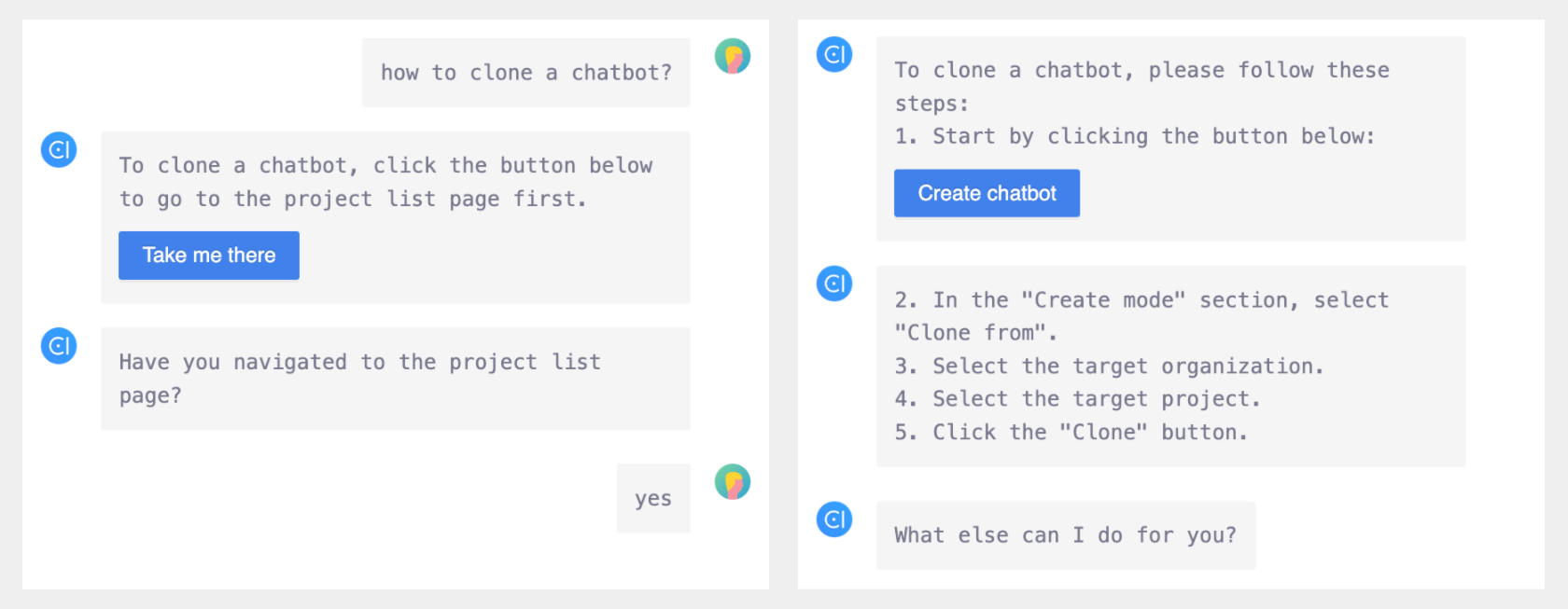
Let's see how to build this skill by following the above steps.
1. Create a new skill: CloneProject
In chatbot ai.bethere.quickstarts, we create a new skill with label CloneProject and add expression to trigger it.
Details with OpenCUI Copilot as an example
- Create a skill with label
CloneProject. - Add the following expressions of this skill:
- How to clone a project?
- How to clone a $type$?
2. Add context
Suppose the action can only be executed when the app user is already on the target page. Therefore, in each component skill, we add a context slot with the type "PageContext" to get the current page.
Details with OpenCUI Copilot as an example
Add the following slot in skill CloneProject:
contextwith typePageContext
3. Add parameters required for the skill
There are two ways to clone a project:
- Enter the target project and click the Clone button to clone it.
- Enter an organization, click the Create button, select the type, and change the clone mode to Clone from.
Since OpenCUI copilot does not support cross-organizational operation for now, copilot can only assist app users in cloning projects using the second method. The parameters required to clone a project include the project type, organization, and label of the target project.
To determine the project type, we created the entity "ProjectType" and added a slot with this type, so copilot can prompt app users to select the project type. However, DU currently cannot understand the organization and project labels. Therefore, only the project type can be obtained from the app users.
Details with OpenCUI Copilot as an example
Add the following slots in skill CloneProject:
typewith typeProjectTypeorgLabelwith typeStringprojectLabelwith typeString
Add annotations for slot type:
- Fill strategy: Always ask
- Prompt: Which kind of project would you like to clone?
4. Add slot to verify the current page
As we can obtain the current page through the context slot, we add a boolean slot called isTargetPage. It is initialized as true if the app users are on the target page, and false otherwise. We also add a value check annotation. If the app users are not on the target page, we provide an action button for them to navigate to the target page.
Details with OpenCUI Copilot as an example
Add the following slot in skill CloneProject:
isTargetPagewith typeboolean
Add annotations for slot isTargetPage:
- Fill strategy: Always ask
- Initialization:
kotlinif (context?.page == "agentList") true else false- Prompt: Have you navigated to the project list page?
- Value check:
- Condition:
kotlinisTargetPage == true- Template:
json{ "type": "rich", "description": "To clone a ${type!!.expression()}, click the button below to go to the project list page first.", "insideAction": [ { "type": "click", "display": "Take me there", "payload": { "clickAction": "page", "targetPage": "agentList", "orgLabel": "${context?.orgLabel}" } }] }
5. Add response (frontend action button)
Finally, after collecting all the required parameters, we can generate an action button to clone a project. Since the app users cannot fill the orgLabel and projectLabel slots, the default action of this skill will not mention the target organization and project. However, if these slots are initialized by other composite skills, there is a chance that they can be filled. Therefore, we added a branch to handle that situation.
Details with OpenCUI Copilot as an example
Add a default response in skill CloneProject:
- Action: Single value message
json{ "type": "rich", "description": "To clone the \"${projectLabel}\" ${type!!.expression()}, please follow these steps:\n1. Start by clicking the button below:", "insideAction": [ { "type": "click", "display": "Create ${type!!.expression()}", "payload": { "clickAction":"custom", "targetAction": { "action":"createProject", "projectType": "${type!!.value}" } } } ] }- Action: Single value message
text2. In the "Create mode" section, select "Clone from". 3. Select organization: "${orgLabel}". 4. Select project: "${projectLabel}". 5. Click the "Clone" button.Enable branch in the response of skill CloneProject.
Add a branch response in skill CloneProject:
- Condition:
kotlinorgLabel != null && projectLabel != null- Action: Single value message
json{ "type": "rich", "description": "To clone a ${type!!.expression()}, please follow these steps:\n1. Start by clicking the button below:", "insideAction": [ { "type": "click", "display": "Create ${type!!.expression()}", "payload": { "clickAction":"custom", "targetAction": { "action":"createProject", "projectType": "${type!!.value}" } } } ] }- Action: Single value message
text2. In the "Create mode" section, select "Clone from". 3. Select the target organization. 4. Select the target project. 5. Click the "Clone" button.
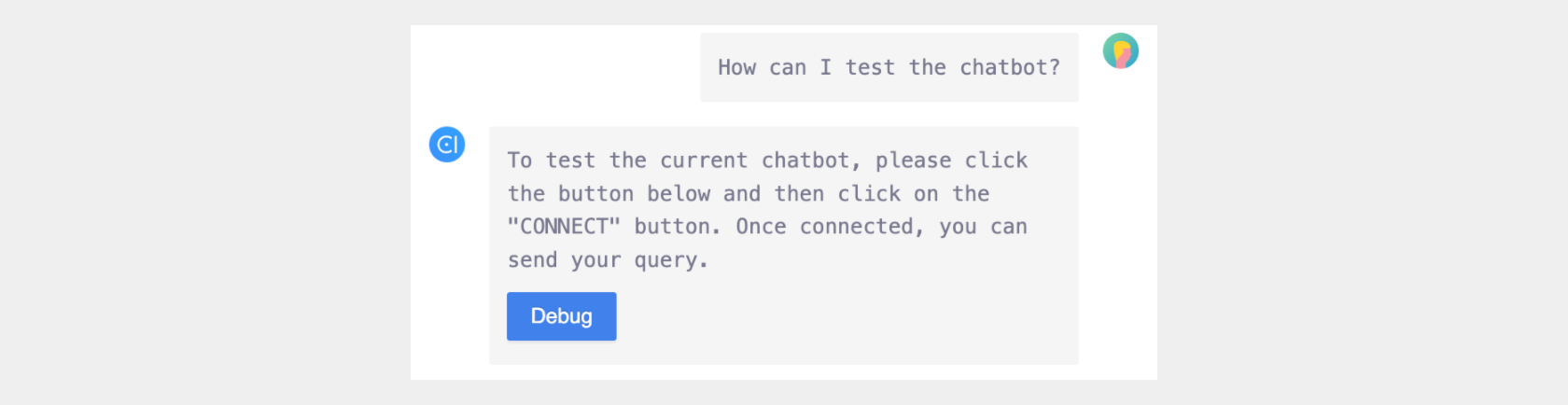
Similarly, the TestChatbot skill can be created. Unlike the CloneProject skill, the debug action can be executed within the chatbot itself. Once app users are in the target chatbot, no parameters are required to execute the debug action.
This is the happy path for TestChatbot skill:
Build a composite skill
To build a composite skill for onboarding app users or combining multiple actions, follow these steps:
- Create a new skill and add the expression to trigger this skill.
- Add component skills required for the onboarding procedure and initialize them with fixed parameters.
- Add dialog annotations to add the missing information if necessary.
- Add slots to verify if the app users have completed each step if necessary.
For example, let's consider the QuickStartClone skill used to guide app users through the process of quickstart cloning an echo chatbot. The happy path for the QuickStartClone skill involves the following steps:
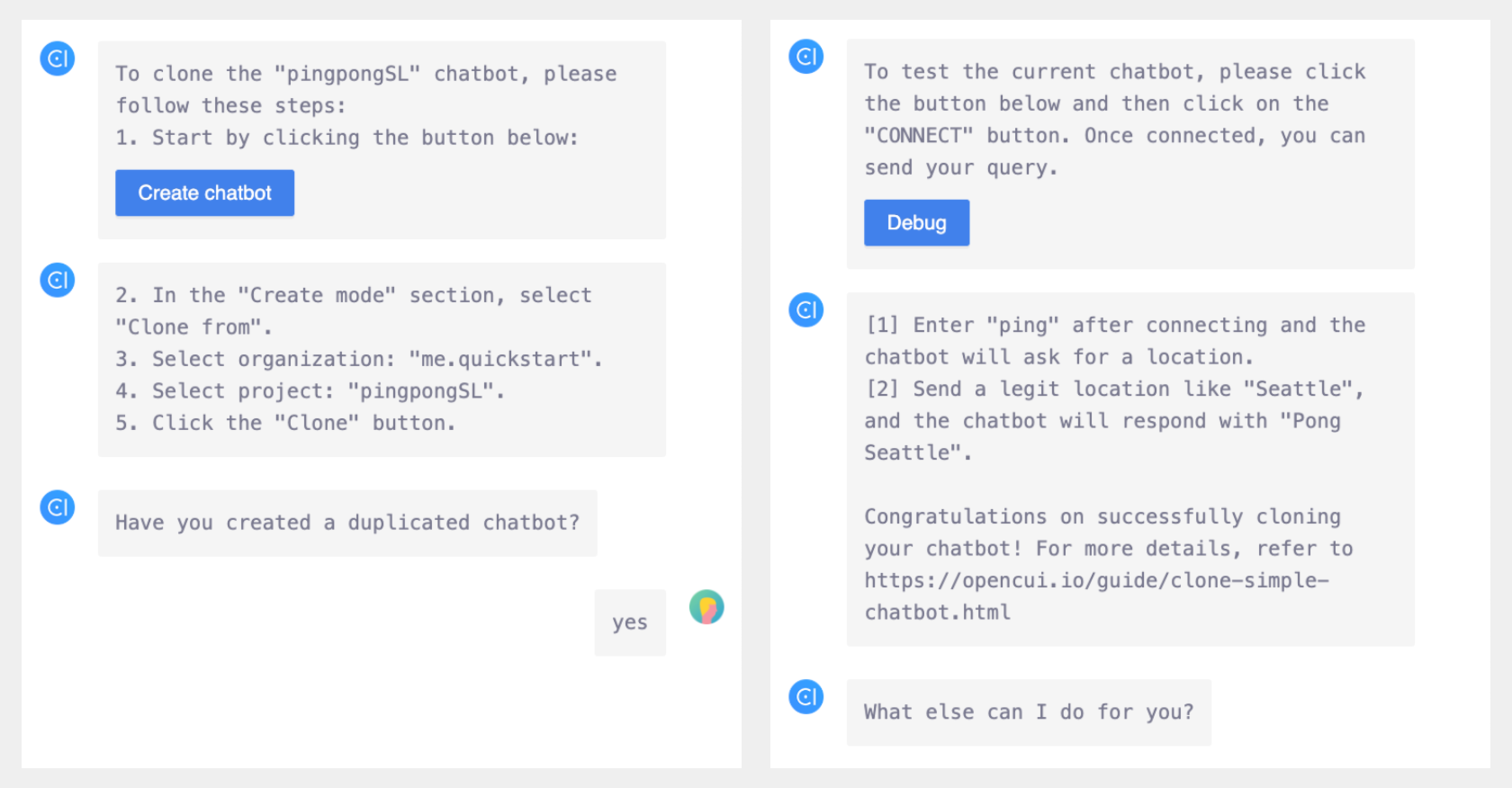
Let's see how to build this skill by following the above steps.
1. Create a new skill: QuickStartClone
In chatbot ai.bethere.quickstarts, we create a new skill with the label "QuickStartClone". Since quickstarts are a series and cloning an echo chatbot is only part of them, we don't expect app users to trigger this skill directly.
Instead, we add this skill as a slot to another composite skill "QuickStartGuide", which can be triggered by app users. Therefore, there is no expression for this skill QuickStartClone.
Details with OpenCUI Copilot as an example
Create a skill with label CloneProject
2. Add component skills
As we've built the skill "CloneProject" and skill "TestChatbot", now we can add these skills as slots in the skill "QuickStartClone". Since the cloned project is fixed in this quickstart, we can use the type-level initialization to initialize the skill CloneProject with the predetermined parameters including project type, organization label and project label.
Details with OpenCUI Copilot as an example
Add the following slots in skill QuickStartClone:
cloneProjectwith typeCloneProjecttestChatbotwith typeTestChatbot
Add type-level initialization for skill QuickStartClone:
- Fill slot
cloneProject.typewith value:ProjectType("chatbot") - Fill slot
cloneProject.orgLabelwith value:"me.quickstart" - Fill slot
cloneProject.projectLabelwith value:"pingpongSL"
- Fill slot
3. Supplement the missing information
In the quickstart cloning an echo chatbot, there is an instruction on what to send to test the chatbot. This instruction is not covered in this skill yet, so we add a post-fill action in the slot testChatbot to supplement the missing instruction. Additionally, as there is no response section for the composite skill currently, we add the concluding part here as well.
Details with OpenCUI Copilot as an example
Add annotation post-fill action for slot testChatbot:
Condition:
kotlintrueTemplate:
[1] Enter "ping" after connecting and the chatbot will ask for a location.
[2] Send a legit location like "Seattle", and the chatbot will respond with "Pong Seattle".
Congratulations on successfully cloning your chatbot! For more details, refer to https://opencui.io/guide/clone-simple-chatbot.html
4. Add slots to check the cloning step
To ensure that app users complete each step of the cloning process, it's helpful to guide them through the steps one by one. After showing them how to clone the echo chatbot, we want to confirm if they have finished this step. To achieve this, we add a boolean slot. If their answer is negative, copilot will prompt them to complete the cloning step before proceeding to the next step.
Details with OpenCUI Copilot as an example
Add the following slot in skill CloneProject:
isNewChatbotPagewith typeboolean
Add annotation for slot isTargetPage:
- Fill strategy: Always ask
- Prompt: Have you created a duplicated chatbot?
- Value check:
- Condition:
kotlinisNewChatbotPage == true- Template: Before proceeding to the next step, please follow the steps provided above to clone the chatbot first.
