State transition
The 5 stage slot filling is designed to minimize builders' effort level in building the conversational experience that get collaborative user served as fast as possible, under the favorable conditions. As such, the bot will follow a deterministic interaction logic that first determines a user's intent, triggers the corresponding skill and then aggressively fills slots of that skill one by one until it has all the required parameters to invoke the service.
However, the design bias towards favorable conditions in these standard slot filling components can sometime cumbersome for interaction logic for unhappy use case. For example, when a user wants to buy a ticket, the movie he wants is sold out. Instead of asking what showtime he likes, whether he wants IMAX, it is a better experience to simply exit conversation early:
User: "Two tickets for Star Wars please?"
Chatbot: "Sorry all tickets are sold out today. What else can I do for you?"Overview
The 5 stage slot filling conversational interaction logic defined by chatbot builder in intentionally modeled under dynamic state chart, or dynamic composite state machines. The deterministic nature warranted by this conceptual model make it easy for business to control interaction logic for their business needs, both in building and debugging phase.
In particular, each entity slot filling is essentially a deterministic state machine, that deterministically move from the start state to end state, that go through the 5 stages of slot filling based the transition table defined by corresponding CUI components. The frame slots are filled by a composite state machine that also includes the type-level CUI component, as well as the components defined on each one of its slots.
Transition is a low level annotation that give builder the ability to control the state machine directly. It is an optional type level annotation which lets you define transitions between slots hosted directly and indirectly by hosting frame.
Transition can be configured in two parts: triggering and update actions, where triggering defines under what condition the corresponding actions sequence is executed.

Transitions
Currently, we support two kinds of transitions: event triggered transitions and condition triggered transitions.
Event triggered transitions
Given skill, the interaction logic or transition table defined by slot filling components will always try to proactively fill every it's slot, and delivery the result to user based on the filled slots. While direct slot filling is already capable for many real world use case, many advanced use cases involves no-direct slot filling.
For example, during a purchase session, the user might want to use a certain coupon by say "use the coupon that will expire soon". Instead of responding with "I do not know what you are talking about", you can set up an event triggered transition, with triggering event set to be "CouponSelection", and actions include a fill action which can assign the coupon code that is returned from a function that retrieves the expiring coupon code for given user.
Chatbot: "Okay lets go ahead and begin checkout."
User: "I want to use the coupon that will expire soon."
Chatbot: "Sure. Would you like to use the credit card on file?"The triggering part of event triggerred transition are defined by arbitrary frame event, and update can be any valid action sequence.
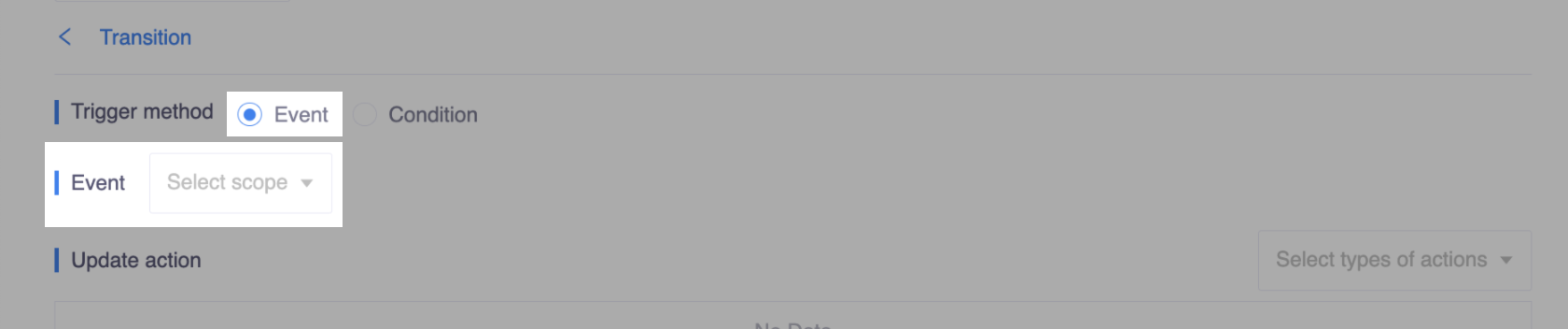
Condition triggered transitions
The default behavior of slot filling after one slot is filled is always moving onto fill the next slot. But sometime, this behavior is not what you want. In addition to early exit example at the beginning of this doc, condition triggerred transition can also be used for looping back.
For example, a user want to get some food, say you have a taxonomy of food arranged into some tree structure, you can use condition triggerred transition for a while loop kind of conversational experience. Here, as long as the food user specified is not concrete food, but some category, we can jump back and ask user to clarify:
User: "I like order some Chinese food."
Chatbot: "Cool, what food do you want? We have noodle or rice as main dish."
User: "noodle please."
Chatbot: "Sure, what noodle do you want? we have dry noodle or noodle soup."Condition triggerred transition allows you to customize interaction logic based on slot values. The triggering part is defined by triggering timing and triggering condition, where timing is defined by a slot, and triggering condition can be specified by arbitrary boolean Kotlin expression. When the trigger timing slot is filled and the condition expression evaluates to true, the corresponding actions will be executed.

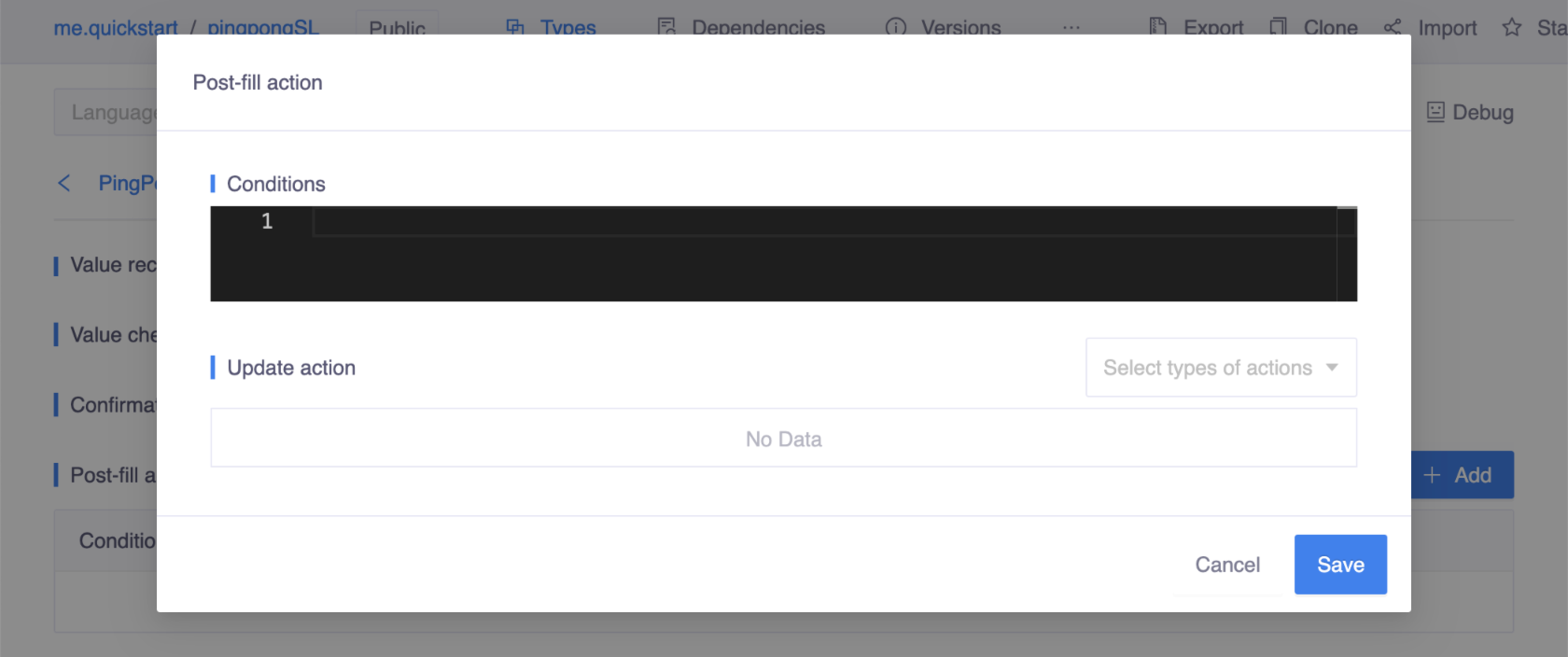
There is a convenient shortcut for condition triggered transitions at the slot level, which can be set in the target slot. The target slot refers to the slot you choose for specifying the trigger timing. To set it at the slot level:
- Enter the target slot, and switch to the Annotation tab. Enable Post-fill action and click the Add button.
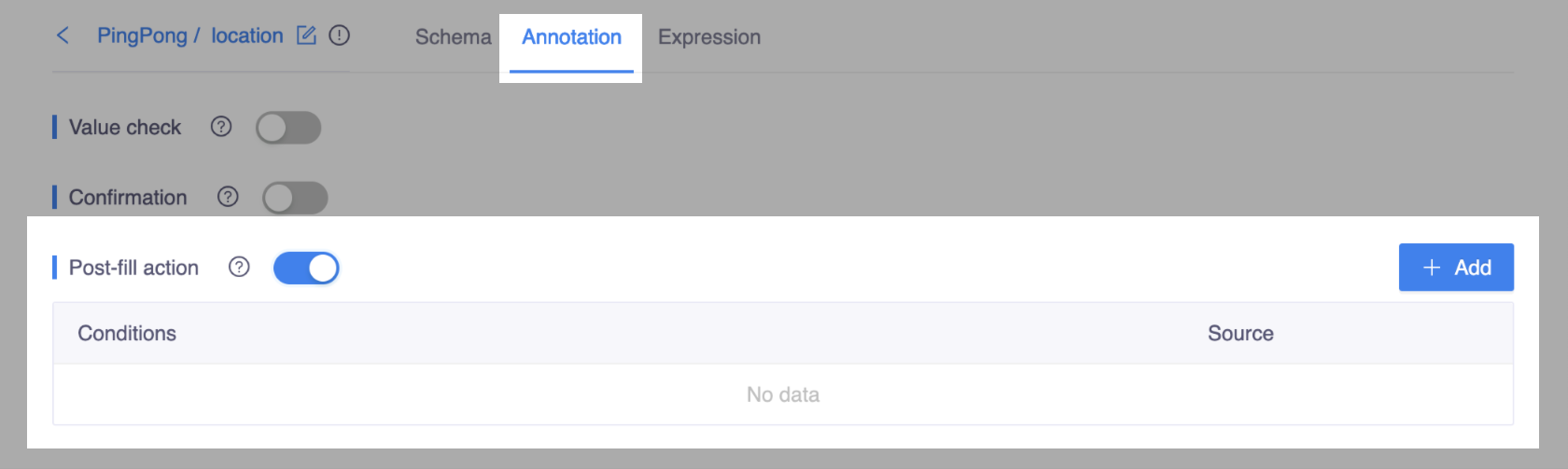
- In the popup window, enter the Conditions using Kotlin expressions and select the desired Update action.
Used with caution
Transition is a low level control that you can use to implement arbitrary conversational interaction logic. But with great power, comes with great responsibility. The low level control can adversely impact the interaction logic defined at slot filling level if not used carefully. Please test your design when it comes to transition.
System actions
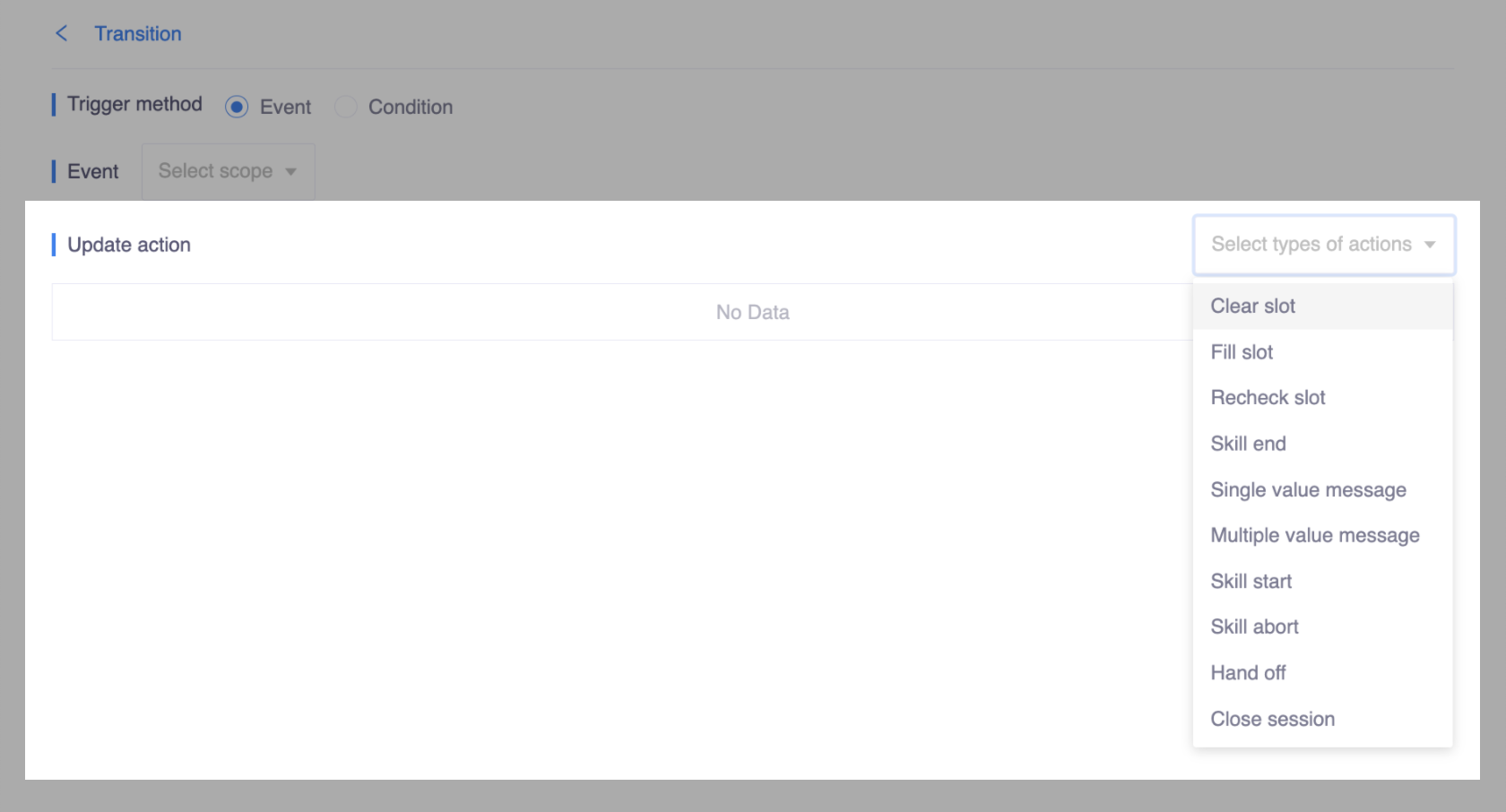
Update action contains one or more actions in sequence, you need to define it by order. When the trigger is active, bot will respond the update action one by one according to the top-to-bottom order, please make sure the order of actions is the one you want.
With actions, you can:
- Prompt users for necessary information by Single value message and Multiple value message. See Universal channel for more details about messages;
- Change the state of slot filling by Clear slot, Fill slot and Recheck slot;
- Transfer conversation by Skill start, Skill abort and Skill end.
Single value message
Prompt user a static text or media reply, it can be used to verbalize a single value of some type. This type of message can only support tuple (think of static list where the number of elements are known at build time).
Multiple value message
Prompt user a dynamic list reply, it is designed to verbalize multiple value of some time, where the number of elements are not know at build time. The multiple value message bind to a list of some type, and can be expressed via code expression for maximal flexibility.
Clear slot
Clear the target slot's value, which needs to be refilled according to the setting of slot filling stages. It is a good way to use in cooperation with Recheck slot, to make sure some value still makes business sense.
Fill slot
Assign the value expressed in code expression to target slot, which supports the following expressions:
Constant: For example, if the type of target slot is
kotlin.Int, you can associate the value with1; If the type of target slot is multi-valuedkotlin.Int, you can associate the value to belistOf(1, 2, 3).Slot: You can pick an earlier slot of the same type as proposed value, for example
slotA. If you pick a later slot, the behavior is not defined, meaning the behavior might change without notice.Function call: You can set the target slot
phoneNumberby using function label directly, such asgetUserPhoneNumber().
Of course, expression can be arbitrarily nested via method calls, and combined via operators, such as if expression, when expression, !! operator, Elvis operator, for more details you can see Kotlin expression.
Note
When use Fill slot with code expression, you should ensure that assignment actually works. For instance, the code expression should be valid for the current context.
Recheck slot
Move the stage before checking the value of target slot, to make sure it still makes business sense. OpenCUI reset every slot after slot to be cleared to be rechecked by default.
Skill start
Start a new skill with its slot filled with assignments by code expression, when this expression is evaluated to not null, the new started skill will skip the interaction on these slots.
Skill abort
Abort the skill you specified. Abort is treated as abnormal termination which indicates all associated or nested skills will be affected. For example, if you provide a round-trip booking service by using composite skill which contains flight skill, and there is no suitable flight available, you can make a decision to abort skill. If the flight skill aborted, the round-trip composite skill will be assumed the same way.
Skill end
Terminate the current skill. For example, when the ticket that the user wants to buy has been sold out, it is a better experience to simply exit conversation early with condition triggerred transition by adding skill end action. Of course, you'd better add some replies at the same time to remind the user context. Skill end will only terminate the current skill and will not affect others.
Hand off
Transfer the current conversation to a human agent. Please make sure you have configured Support.
Close session
Clear the entire session. For example, if the bot gets stuck with the user, for a better experience, the bot should actively jump out of the stuck and restart with the user under pre-set conditions.
