Fill strategy
Fill strategy is the rule that determines how to interact with the user to obtain the information needed to complete a service. It decides whether or not to prompt the user for the information, and it also defines how other dialog annotations should work together.
A slot is a piece of information that is needed to complete a task. For example, in a restaurant reservation service, the slots might be date, time, and number of guests. When you set the fill strategy to a slot and it is configured to be filled by user interaction, you can configure the dialog annotations based on your business logic. The OpenCUI framework will use a five-stage slot filling process to help you interact with users and converge on a servable request.
The best fill strategy to use will depend on the specific task and your business needs. By understanding the different fill strategies, you can choose the one that is most likely to result in a successful interaction.
Here is a more detailed explanation of each fill strategy.
Always ask
Always ask strategy is a good choice for scenarios where users are required to provide essential information. It is a robust strategy, meaning that if the user does not provide the information, the chatbot will continue to ask until it gets what it needs. The always ask strategy can be helpful in ensuring that the chatbot has all of the information it needs to complete the service.
When you set the fill strategy to always ask, it is important to provide at least one prompt. Prompts are questions that can be used to ask users for information. They should be relevant to the information that you are asking for, clear and concise, and easy for the user to understand.
For example, if you are creating a chatbot that helps users book a table at a restaurant, you might use the following prompt: "What time would you like to book your table?" If you do not provide any prompts, the chatbot will not be able to ask the user for the information that you need. This could lead to the conversation getting stuck, or it could result in the chatbot providing incorrect information to the user.
More detailed explanation of how to set the Always ask strategy
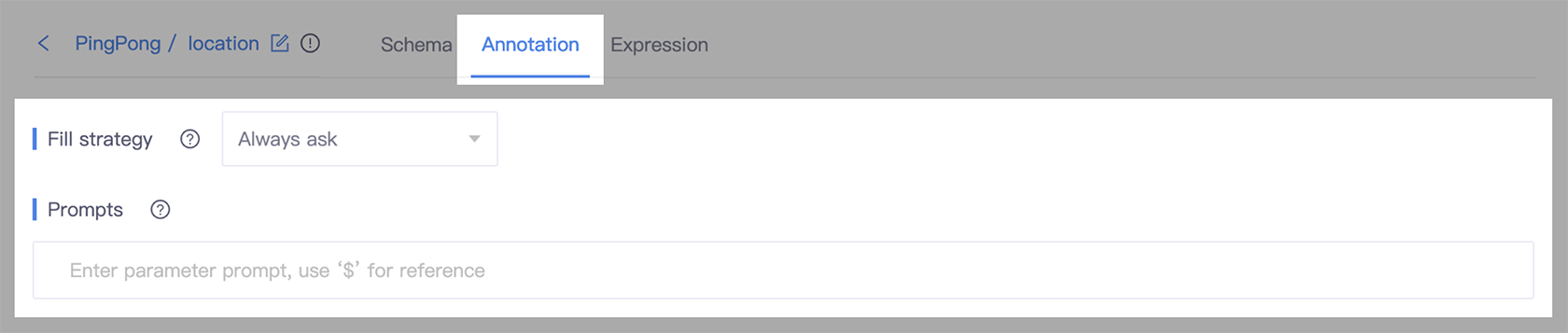
- Go to the slot detail page, and select the Annotation tab.
- In the Fill strategy section, select Always ask.
- In the Prompt field, enter the question that can be used to ask users for information.
Conditional
Conditional strategy is a good choice for scenarios where users are required to provide essential information, but only under specific conditions. It is not as robust as the always ask strategy, as it needs to meet the conditions before asking the user for information. The conditional strategy can be helpful in ensuring that the chatbot only asks for information that is relevant to the task at hand.
When you set the fill strategy to conditional, you should specify the condition and include at least one prompt. The condition is an expression that determines whether or not the chatbot should ask the user.
For example, if you are creating a chatbot that helps users book a table at a restaurant, you might use the conditional strategy for the slot that stores the name of the event. The condition could be that the number of guests is greater than 10:
// If the user wants to book a table for more than 10 people, ask for the name of the event
numberOfGuest > 10If the condition is met, the chatbot would ask the user for the name of the event. If the condition is not met, the chatbot would not ask the user for the name of the event.
More detailed explanation of how to set the Conditional strategy
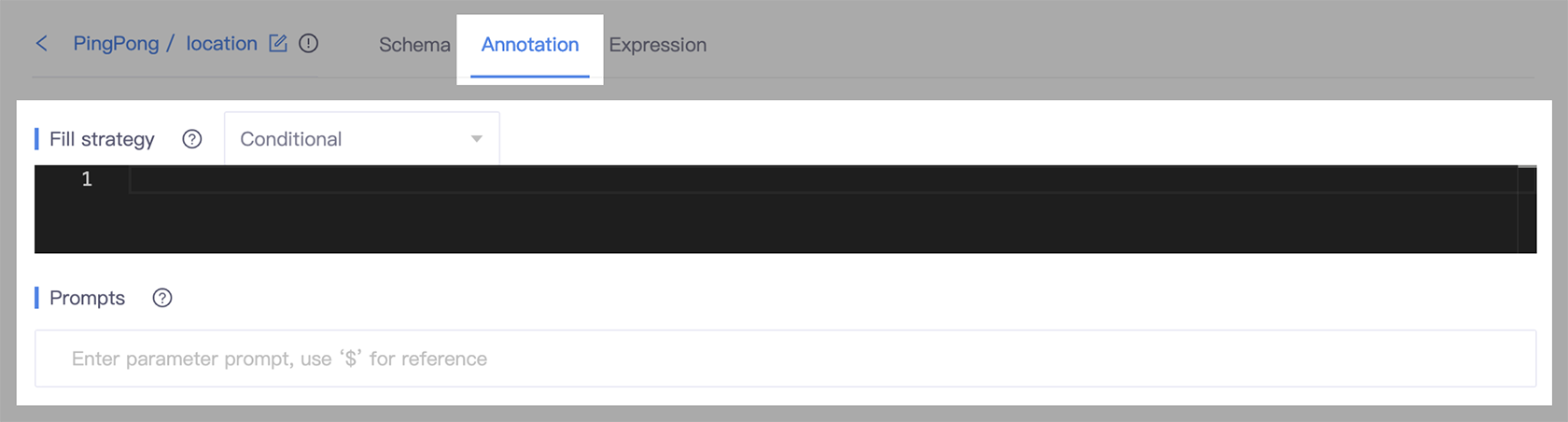
- Go to the slot detail page, and select the Annotation tab.
- In the Fill strategy section, select Conditional.
- In the Condition field, enter the expression that determines whether or not the chatbot should ask. The expression can be a simple comparison, such as
numberOfGuests > 10, or it can be a more complex expression, such asnumberOfGuests > 10 && timeOfDay == "evening". - In the Prompt field, enter the question that can be used to ask users for information.
Gated
Gated strategy is a boolean gate that is used to first introduce a topic before asking detailed questions about it. It can be a helpful way to ensure that the chatbot is only asking questions that are relevant to the user's needs. It can also be especially useful in situations where the user may be sensitive about the information they are providing, as it allows the user to control how much information they share.
The Gated strategy can only be applied to frame slots. Therefore, to take advantage of this strategy, you first need to define a frame to host closely related slots. When you set the fill strategy to Gated, you should provide the boolean gate question.
The Gated strategy will ask the user a yes-or-no question once and then wait for one of three types of answers:
Yes: If the user answers yes, the chatbot will follow the depth-first rule and start filling nested slots one at a time in their natural order.
Slot value: If the user answers with a slot value, the chatbot will assume the gate is open and start filling nested slots with the user's input.
No: If the user answers no, the frame slot will simply be skipped (neither asked nor filled).
For example, if you want to find out what symptoms a patient has, a chatbot can ask about symptoms in a more polite and sensitive way by first asking the patient whether they have any symptoms such as "Do you have any symptoms?". If the patient says yes, the chatbot could then ask more detailed questions about the symptom: "How long have you had a fever?", "Is it intermittent or continuous?", "What is your highest recorded temperature?" If the patient says no, the chatbot can move on to the next topic.
This can help to improve the user experience by ensuring that the chatbot only asks for the information that is relevant to the user's needs.
More detailed explanation of how to set the Gated strategy
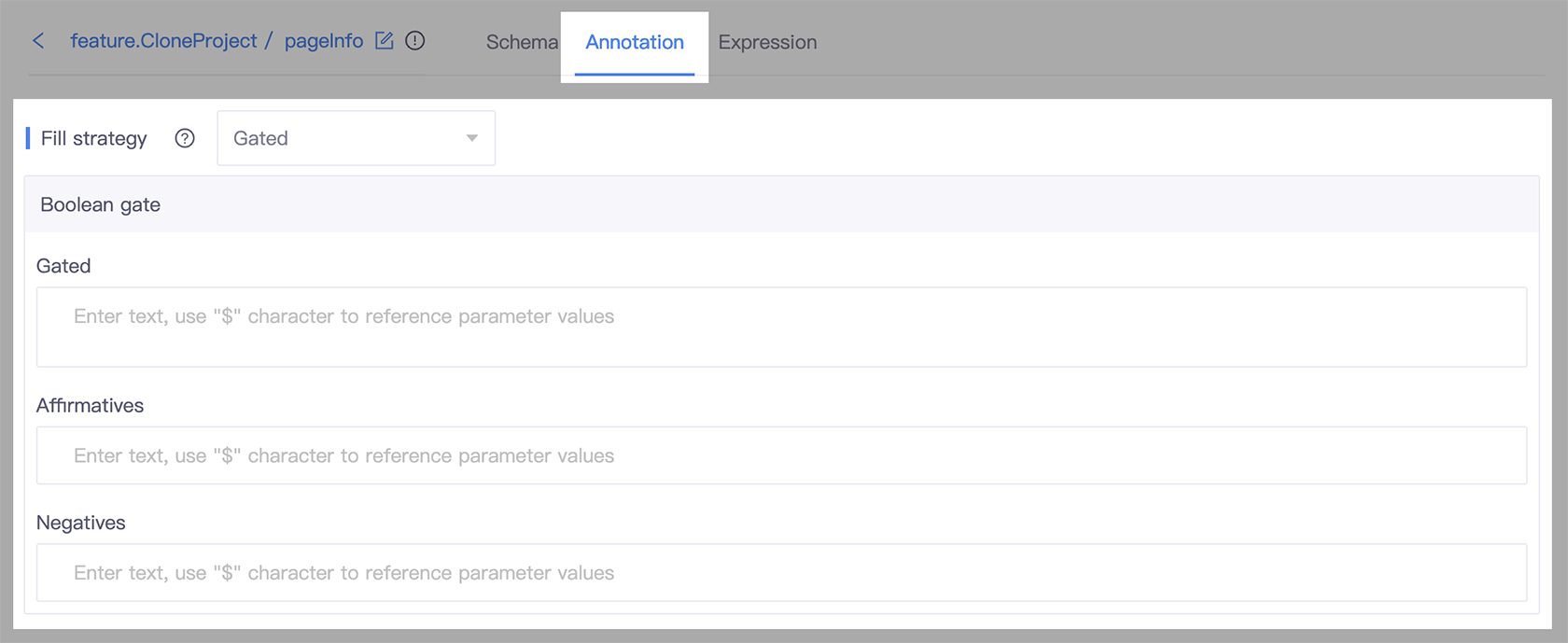
- Go to the slot detail page, and select the Annotation tab.
- In the Fill strategy section, select Gated.
- In the Gated field, provide the boolean gate question.
- In Affirmatives and Negatives field, you can customize how the system understands user utterances that are interpreted as
yesornobased context.
Recover only
Recover only strategy is a way to protect user privacy and make chatbots more user-friendly. It means that the chatbot will not ask the user for information unless the user specifically provides it.
For example, if a business does not need to know the user's age, they can use the Recover only strategy. This means that the chatbot will not ask the user for their age unless the user says something like "I am 25 years old".
When you set the fill strategy to recover only, you should fill in at least one prompt. This is to ensure that the chatbot can handle unexpected input from the user. The prompt will only be used if the chatbot cannot understand the user's input or if the slot value fails the value check.
More detailed explanation of how to set the Recover only strategy
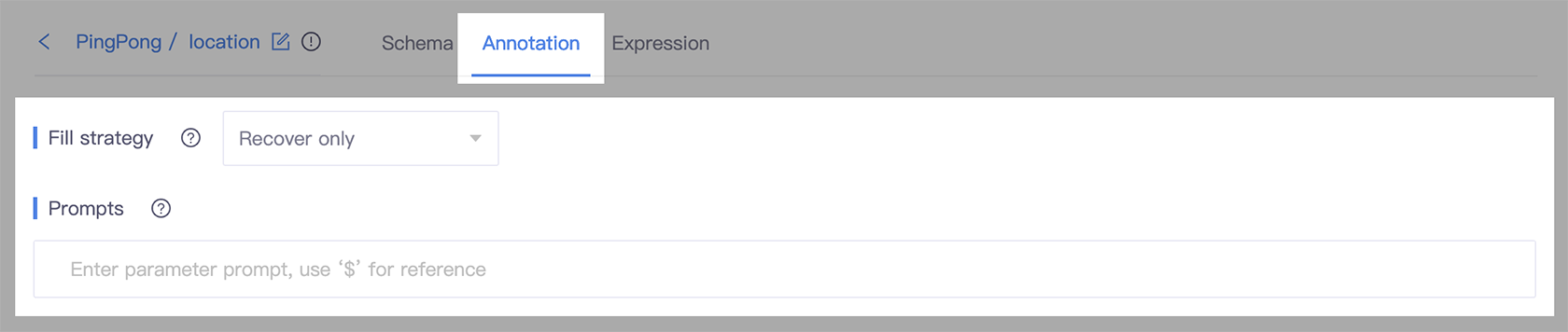
- Go to the slot detail page, and select the Annotation tab.
- In the Fill strategy section, select Recover only.
- In the Prompt field, enter the question that can be used to ask users for information.
The Recover only strategy can be useful for the following use cases:
When the business has a default behavior or choice that could satisfy most users. If the user does not provide any information, the chatbot will use the default behavior or choice. However, if the user does provide information, the chatbot will use that information instead.
When the business has a behavior or choice that they do not want to promote, but they still need to handle if it is required. For example, a business may not want to promote a specific product, but they still need to handle it if the user asks about it.
Direct fill
Direct fill means that the chatbot will not ask the user for information. Instead, it will fill the value directly from a source, such as a database or other slot. This can be helpful in situations where the information is easily accessible and does not need to be collected from the user.
For example, if a chatbot is connected to a database of customer information, it can use the direct fill strategy to fill the slot for the user's name. The chatbot would not need to ask the user for their name, as it can simply retrieve the name from the database.
The direct fill strategy can be useful for reducing the number of questions that the chatbot asks, improving the accuracy of the information, making the chatbot more scalable. However, it does not ask the user if the value is problematic. This means that the chatbot may fill the slot with incorrect or outdated information. This can be a drawback in some cases, such as when the information is sensitive or confidential.
More detailed explanation of how to set the Direct fill strategy
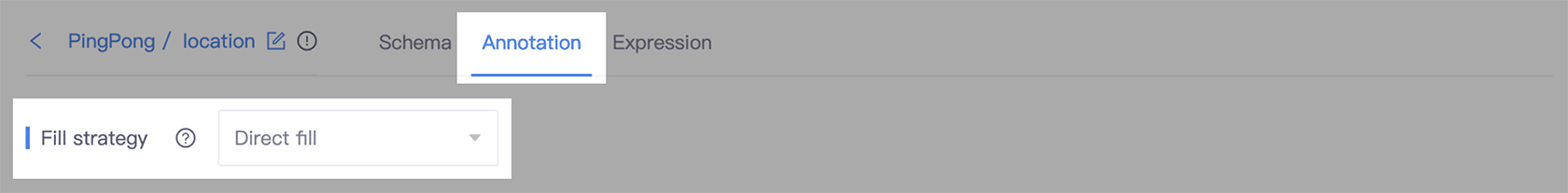
- Go to the slot detail page, and select the Annotation tab.
- In the Fill strategy section, select Direct fill.
External event
The External event strategy means that the chatbot will not fill the slot with information itself. Instead, it will wait for an external event to occur before filling the slot. This can be useful in situations where the chatbot needs to work with external software, such as a payment processor or other asynchronous events.
For example, if a chatbot is trying to book a flight, it can use the external event strategy to wait for the user to complete the payment process. Once the payment is complete, the chatbot will receive an event from the payment processor and then fill the slot with the flight information.
When you set fill strategy to external event, you should:
Provide a message to inform the user of the conversation state. This should let the user know the chatbot is waiting for an external event to occur before filling the slot.
Configure the third-party software to send an event to resume the skill. Different third-party software have different mechanisms for doing this.
Handle errors that may occur when the external event does not occur or when the event is received incorrectly. For example, you may need to retry the request or notify the user that the booking could not be completed.
More detailed explanation of how to set the External event strategy
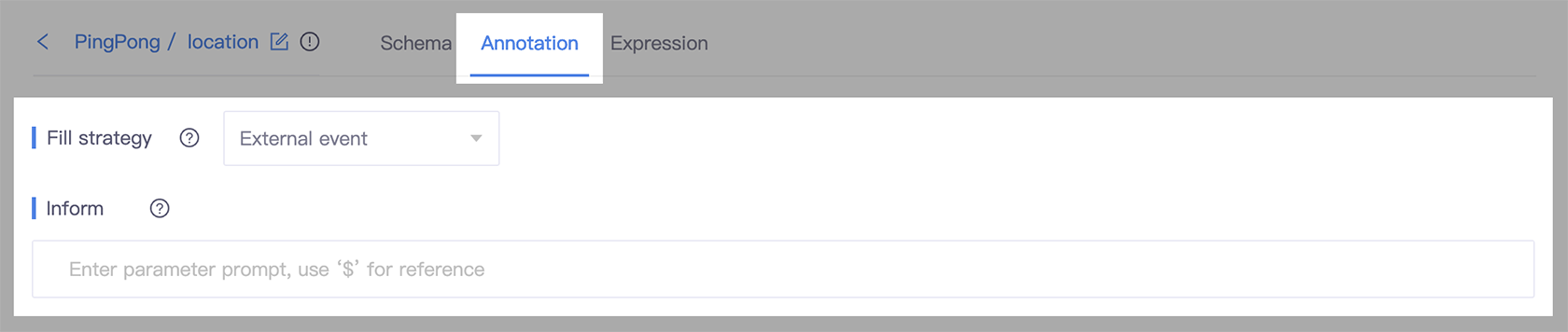
- Go to the slot detail page, and select the Annotation tab.
- In the Fill strategy section, select External event.
- In the Inform field, provide a message to inform the user of the conversation state.
