Value recommendation
Value recommendations are a way to provide users with a list of choices that are likely to be of interest to them. This can be helpful in minimizing confusion, making it easier to answer questions, and making better decisions.
Value recommendations can be based on a variety of factors, such as the current context, the user's past behavior, or their interests. For example, a chatbot that helps users book vacations could provide them with a list of recommendations based on their past travel history, their budget, and their preferred destinations. This can help them to narrow down their choices and find the perfect vacation for them.
By providing users with relevant and helpful recommendations, businesses can help users to find what they are looking for more quickly and easily. This can lead to increased satisfaction and loyalty, as well as more sales.
Overview
Value recommendation is a way to help users choose from a smaller set of pre-approved values by the business, instead of having to go through multiple rounds of trial and error. This is useful when a slot has a large set of potentially valid values from the user side, but a much more restrictive set of values that are actually servable from the business side.
To set up value recommendation, you need to specify the source and the display:
Source
This is the location of the list of values that you want to recommend. You can specify a code expression or skill that returns a list of values of the target type.
In the code expression, you can call service functions such as
function()orfunction(input: slot!!)and optionally apply some post-processing in Kotlin. If the service function returns only up-to-date options, dynamic suggestions will be offered. However, you can even specify a static list if it makes business sense. For example, you could specify the following list of colors:listOf(Color.Red, Color.Black).For a better user experience, the candidates in this list should only include the options that are servable according to the business logic or data.
Display
This is how the bot will render the list of options to the user. You can specify a template that verbalizes the offer list in different languages. The template should include a header, body, and footer. The body is required.
More detailed explanation of how to set value recommendations
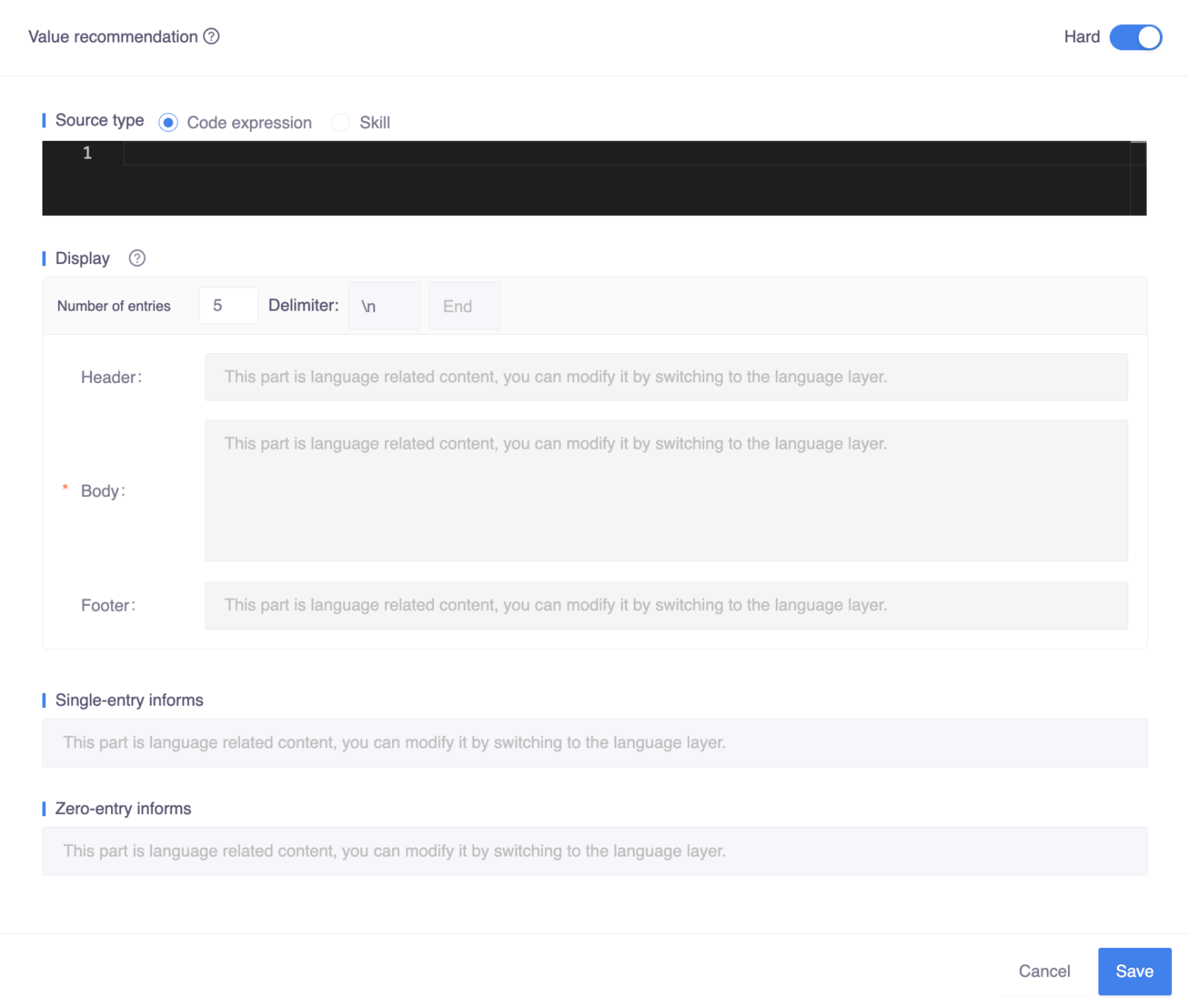
- Source: This is the location of the list of values that you want to recommend. It can be a code expression, or a skill.
- Display: This is how the list of recommended values will be displayed to the user. You can specify the following properties:
- Header: The title content of the recommended card, such as "Top picks for you" or "Recommended for you".
- Body: This is the main content of the recommended card. It should be a text with code expressions embedded. The syntax of the body needs to follow certain rules:kotlin
// This code expression will be replaced with the index of the current item, starting from 1. ${it.index + 1} // Refer entity type, this code expression will be replaced with the expression of the current item. ${it.value!!.expression()} // Refer frame type, this code expression will be replaced with the value of the current item. ${it!!.value} - Footer: This is the text that appears at the bottom of the recommended card.
- Number of entries: The number of items displayed per page. The default value is 5, but it can be modified to any value. However, the value should be considered with the channel that the bot will eventually deploy.
- Delimiter: This is the character that will be used to separate the items in the recommended card. There are two sub-fields:
- The first sub-field is used to define the delimiter between entries. The default value is a newline character
\n, but it can be changed to any other character. - The second sub-field is used to define the delimiter of the last entry. It can be empty if not needed.
- The first sub-field is used to define the delimiter between entries. The default value is a newline character
Value recommendations can be defined at the slot level or the type level.
Slot level
This means that the value recommendation is specific to a single slot.
For example, you could define a value recommendation for the
departureCityslot that only includes cities that are served by a particular airline.This allows users to incrementally communicate what they want, by only providing the information they know at the moment.
More detailed explanation of how to set it on slot level
- Go to the slot detail page, and select the Annotation tab.
- Enable Value recommendation and click the Add button.
- In the popup window, set the source, display, informs and Save.
Type level
This means that the value recommendation is specific to a type.
For example, you could define a value recommendation for the
roundFlightTickettype that includes thedepartureCityandarrivalCityslots. This means that the bot will recommend possible departure and arrival cities together when the user is booking a round flight ticket.This is a more holistic approach, where the bot will always recommend multiple slots simultaneously, and they will be filled together.
More detailed explanation of how to set it on type level
- On the type level, select the Annotation tab.
- In the Value recommendation section, click the Add button.
- In the popup window, set the source, display, informs and Save.
Ultimately, the decision of whether to define value recommendations at the slot level or the type level depends on your business needs and the user experience you want to create.
Hard and Soft
The type of value recommendation can be hard or soft, and it is controlled by the hard toggle.
Hard value rec
Hard value recommendation means that the list of recommended values is the entire list of valid options for the slot, based on business data. When the hard toggle is enabled, the bot will only recommend values that are in the list of candidates. If the user enters a value that is not in the list of candidates, the bot will not fill the slot with the proposed value. Instead, it will stay at the prompt phase and give the user a default reply.
For example, let's say you are building a chatbot for a movie theater. You could use hard value recommendation for the movie slot. This would mean that the bot would only recommend movies that are currently playing at the theater. If the user enters a movie that is not playing at the theater, the bot would not fill the slot with the proposed movie. Instead, it would stay at the prompt phase and give the user a default reply, such as: "Sorry, we are not currently showing that movie."
There are three different scenarios that can happen when using hard value recommendation:
Multiple entries: This means that multiple items were returned from the source. The bot will display the list of recommended values to the user and let them choose one.
Single entry: This means that there is only one item in the result set. The bot will automatically fill the slot with the single value. When there is only one candidate option from the source, the Single-entry inform will be replied to users. This is essentially an implicit confirmation, where the bot lets users know which option the bot will assume so that both the bot and the user are on the same page.
Zero entry: This means that there are no valid options for the slot. The Zero-entry inform will be replied to users, and then exit the current skill as it can not provide the service anymore. The default behavior for the zero-entry scenario is to exit the current skill. However, you can customize this behavior with the Transition annotation, or go back to prompt for this slot with the Value check.
Soft value rec
Soft value recommendation means that the list of recommended values is a subset of the valid options. When the hard toggle is turned off, the bot will recommend values that are in the list of candidates, but it can also accept values that are not in the list of candidates. This means that the user has the option to enter a value that is not in the list of candidates, and the bot will try to fill the slot with the proposed value.
For example, let's say you are building a chatbot for a restaurant. You could use soft value recommendation for the cuisine slot. This would mean that the bot would recommend a list of popular cuisines, such as Italian, Chinese, and Mexican. However, the bot would also accept any other cuisine that the user enters.
This can be useful if you want to give the user the flexibility to enter any value. However, it is important to note that this can also lead to errors, as the bot may not be able to fill the slot with the proposed value.
Page selectable
It is common for a value recommendation to return more than one page of items. When the list is long, it is important to support page navigation interactions, such as:
- "Is there more options?" to go to the next page.
- "Can you go back? I like to see these options again." to go to the previous page.
The page navigation interactions are already supported by the system skill io.opencui.core.PageSelectable. You can customize the understanding behavior for the user's next page expression in io.opencui.core.NextPage, and for the user's previous page expression in io.opencui.core.PreviousPage.
For example, you could customize the understanding behavior for the next page expression by adding the phrase "show me more" or "continue" to the io.opencui.core.NextPage expression section.
Item picker
When there is a list of items, the bot should be able to understand selection expressions, which are used to select an item from the list.
The following behaviors are already supported:
Index expressions: These refer to the item's position in the list per page. For example, the user could say "the first one" or "second" to select the first or second item in the list.
Names: These refer to the item's names. For example, the user could say "the red one" or "the hot one" to select the item that is red or hot.
Don't care expressions: These indicate that the user does not care about the specific item and is willing to accept any item in the list. For example, the user could say "don't care" or "anything will do" to select any item in the list.
These behaviors allow users to interact with the bot in a more natural way, and they can also help the system to better understand the user's intent.
Note
Customization of system skill will not only affect the current slot, but also the entire bot behaviors.
Best practice
If you are considering using value recommendations, there are a few things to keep in mind:
The recommendations should be relevant to the user's needs: The recommendations should be based on the user's current context, their past behavior, or their interests.
The recommendations should be accurate: The recommendations should be based on accurate data.
The recommendations should be up-to-date: The recommendations should be based on the latest data.
The recommendations should be personalized: The recommendations should be tailored to the individual user.
